Introduction
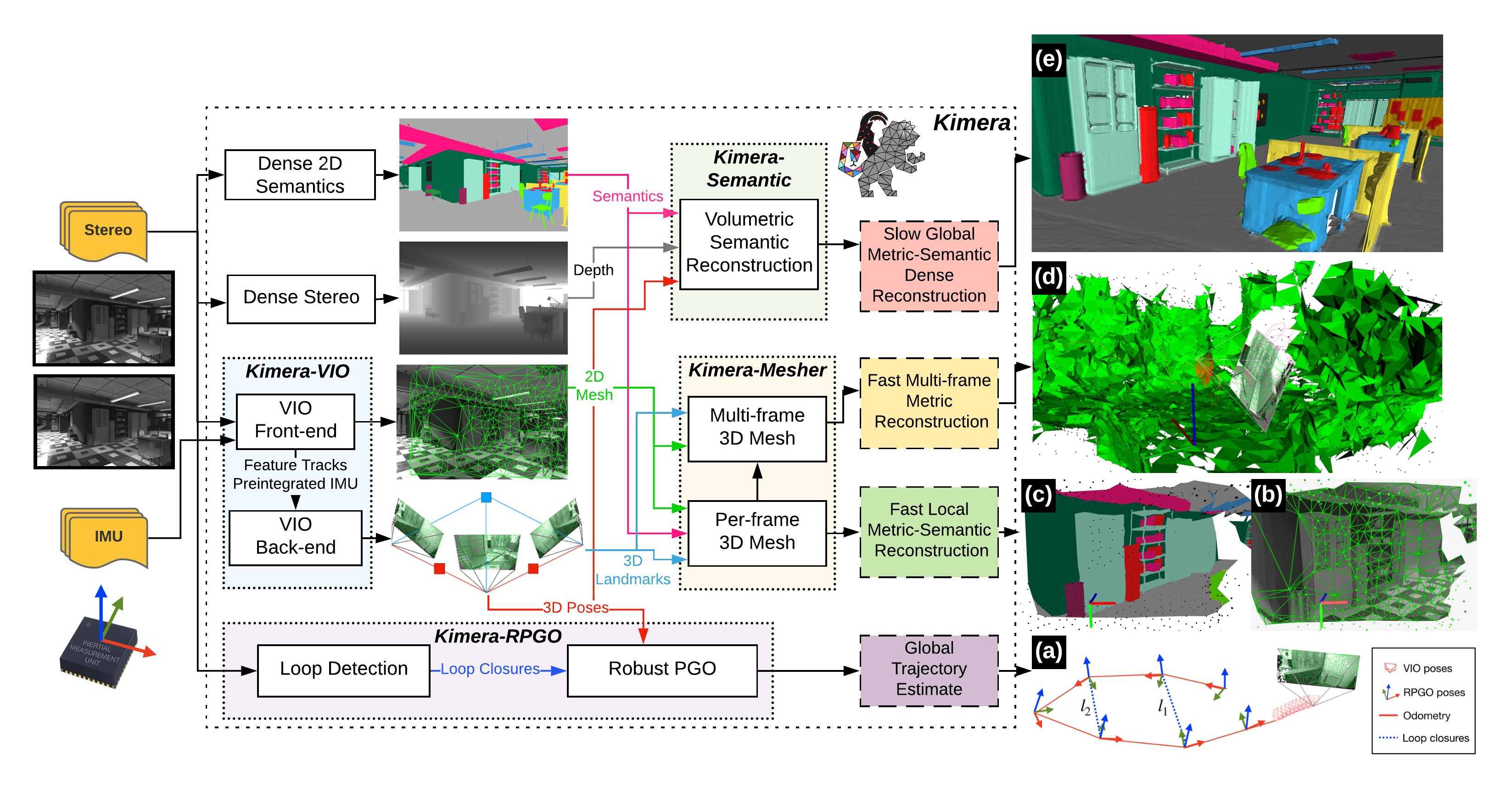
This markdown file explains the steps to generate a 3D real-time mesh reconstruction using Intel RealSense depth camera and Kimera. Kimera is a C++ library for real-time metric-semantic visual Simultaneous Localizaiton and Mapping (SLAM). It consists of four key components: Visual Inertial Odometry (Kimera-VIO), mesh module reconstruction (Kimera-Mesher), robust pose graph optimization (Kimera-RPGO), and 3D semantic segmentaion (Kimera-Semantics). Please, refer to their paper to read more about how all these key components work together. It is a lightweight, robust and efficient library that works on CPU.
General overview of Kimera is as follows:
Tested with ROS Noetic on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Intel Realsense Camera
Kimera uses stereo images and IMU (if available) as an input. I used RealSense D435 depth camera to stream stereo data.
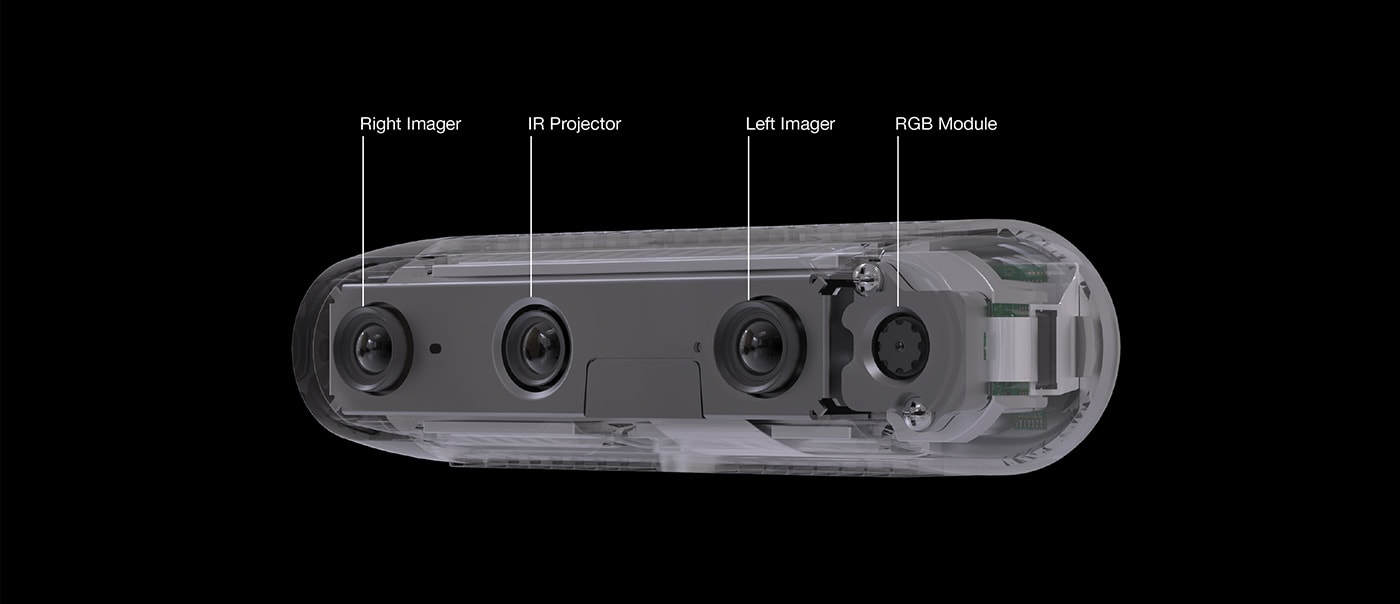
D435 has two stereo cameras with IR projector and RGB camera. Certain models (such as D435i) also have a built-in IMU.
Intel provides SDK for RealSense cameras, which can be downloaded here. The original page provides step by step instructions how to download the SDK for all Operating Systems. It installs RealSense Viewer application, which allows to connect to camera via USB. You can set parameters, stream, take images and update the camera firmware using the application. Additionally, all available drivers for all RealSense cameras can be found here.
The nice thing is this camera have a ROS wrapper which makes it easy to integrate with Kimera.
Install realsense-ros
-
It is possible to install deb package realsense2-camera on Ubuntu.
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-realsense2-camera -
You can build it from source as well.
-
Create a catkin workspace
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src cd ~/catkin_ws/src/ -
Clone realsense-ros repository into ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/IntelRealSense/realsense-ros.git cd realsense-ros/ git checkout `git tag | sort -V | grep -P "^2.\d+\.\d+" | tail -1` cd .. -
Build
catkin_init_workspace cd .. catkin_make clean catkin_make -DCATKIN_ENABLE_TESTING=False -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release catkin_make install -
Automatically source setup bash script when new shell is launched.
echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
-
Launch realsense-ros
In order to start a camera node, you need to start rs_camera.launch file
roslaunch realsense2_camera rs_camera.launch
It will publish several topics depending the on camera type and settings. Typical topics will include raw_image, rbg_image, camera info, imu data etc.
For more information about parameter setup and usage, please, visit: RealSense ROS.
Kimera VIO and Mesher
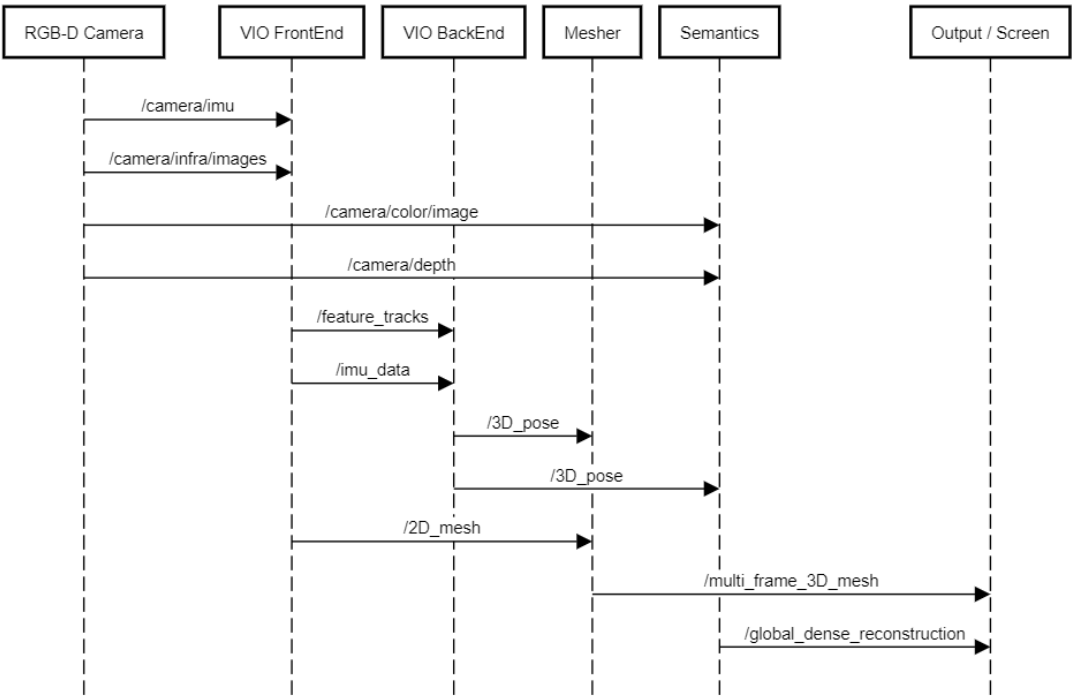
There also exists a ROS wrapper for Kimera too, which makes it significantly easier to pass message from depth camera to Kimera and visualize the results with RViz.
Following diagram shows the basic structure of the wrapper.
Kimera-VIO-ROS installation
-
Besides ROS Neotic (see here), also install non-default dependencies for mesh_rviz_plugins
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-image-geometry ros-melodic-pcl-ros ros-melodic-cv-bridge -
Update package list and install system dependencies
sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends apt-utils sudo apt-get install -y \ cmake build-essential unzip pkg-config autoconf \ libboost-all-dev \ libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev \ # Use libvtk5-dev, libgtk2.0-dev in ubuntu 16.04 \ libvtk6-dev libgtk-3-dev \ libatlas-base-dev gfortran \ libparmetis-dev \ python-wstool python-catkin-tools \ -
ROS wrapper installation (see here)
# Setup catkin workspace mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src cd ~/catkin_ws/ catkin init catkin config --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DGTSAM_TANGENT_PREINTEGRATION=OFF catkin config --merge-devel # Add workspace to bashrc for automatic sourcing of workspace. echo 'source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc # Clone repo cd ~/catkin_ws/src # For ssh: git clone git@github.com:MIT-SPARK/Kimera-VIO-ROS.git # For https: # git clone https://github.com/MIT-SPARK/Kimera-VIO-ROS.git # Install dependencies from rosinstall file using wstool wstool init # Use unless wstool is already initialized # For ssh: wstool merge Kimera-VIO-ROS/install/kimera_vio_ros_ssh.rosinstall # For https # wstool merge Kimera-VIO-ROS/install/kimera_vio_ros_https.rosinstall # download and update repos: wstool updateFinally, compile wrapper with catkin build
catkin build source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
Kimera Semantics installation
-
Install system dependencies
sudo apt-get install python-wstool python-catkin-tools protobuf-compiler autoconf sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-cmake-modules -
ROS wrapper installation
# Setup catkin workspace mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src cd ~/catkin_ws/ catkin init catkin config --extend /opt/ros/melodic # Change `melodic` to your ROS distro catkin config --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release catkin config --merge-devel # Add workspace to bashrc. echo 'source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc # Clone repo cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone git@github.com:MIT-SPARK/Kimera-Semantics.git # Install dependencies from rosinstall file using wstool wstool init # Use unless wstool is already initialized # Optionally add Kimera-Semantics to the rosinstall file # wstool scrape # For ssh: wstool merge Kimera-Semantics/install/kimera_semantics_ssh.rosinstall # For https: #wstool merge Kimera-Semantics/install/kimera_semantics_https.rosinstall # Download and update all dependencies wstool update
Then, compile:
```
catkin build kimera_semantics_ros
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
```
Usage
Before using the real camera, we can test Kimera with Euroc rosbag. In four different terminals, run the fo llowing commands:
roslaunch kimera_vio_ros kimera_vio_ros_euroc.launch run_stereo_dense:=true
roslaunch kimera_semantics_ros kimera_semantics_euroc.launch
rviz -d kimera_semantics_euroc.rviz
rosbag play V1_01_easy.bag --clock
Reconstruction results with both Euroc dataset and RealSense D435 depth camera are as follows:
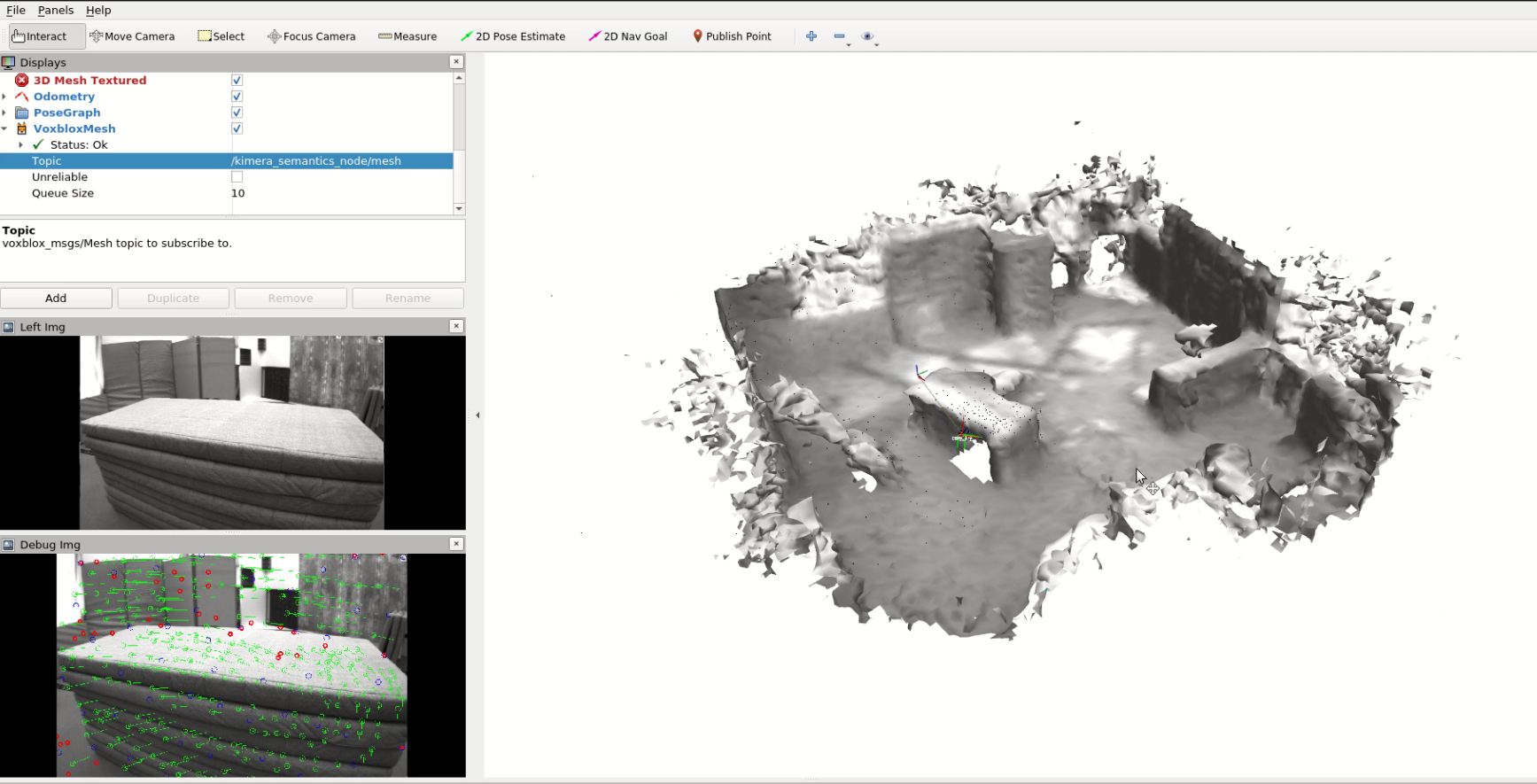
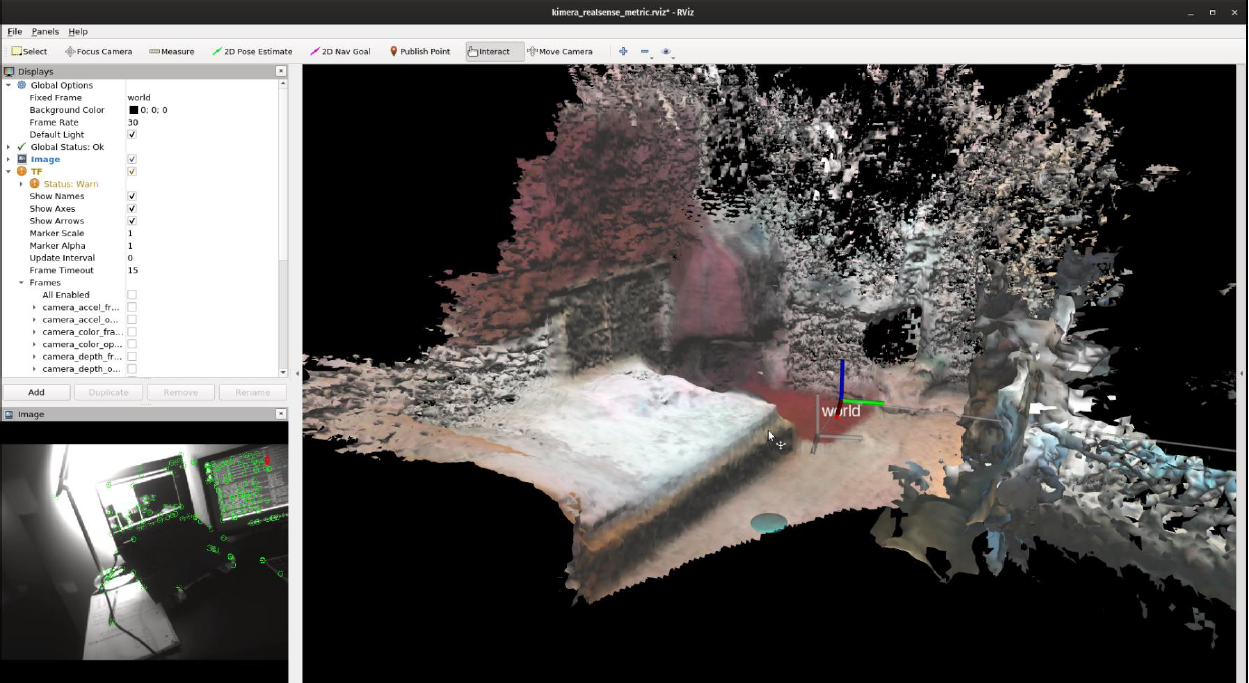
Euroc Dataset Video Demo
Real-time Reconstruction Video Demo


